
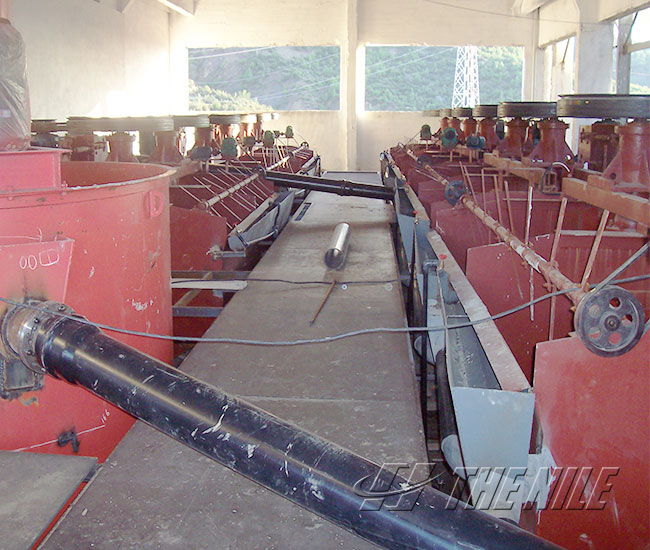
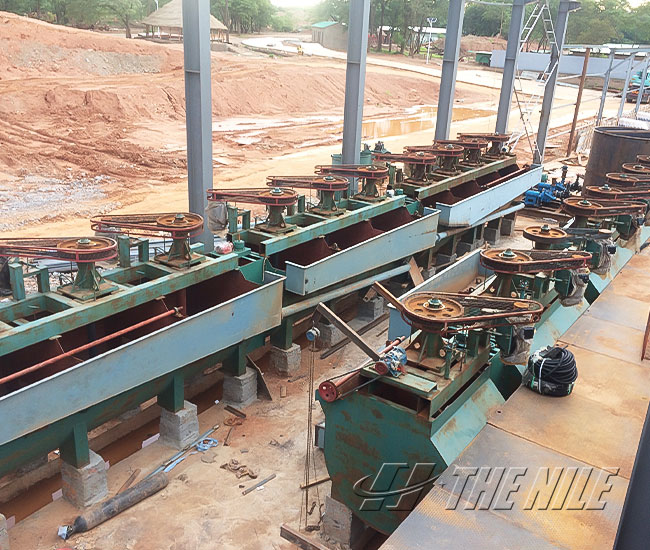
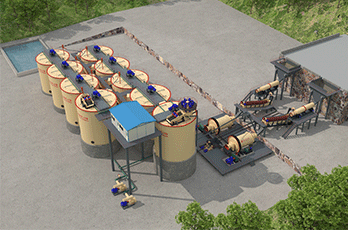
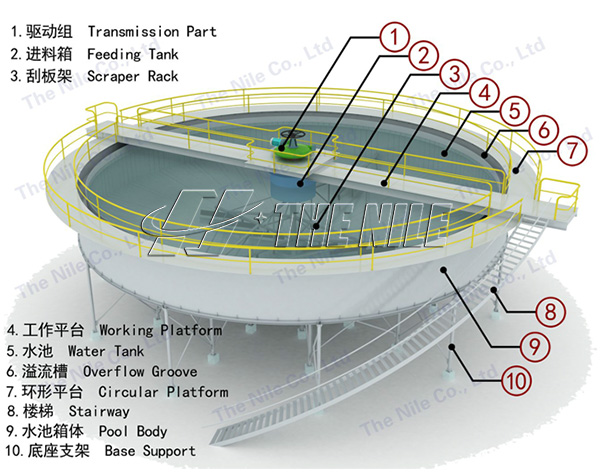
Flotation production line
It has the features of wide application range and strong adaptability.. It can be used in various mineral departments such as nonferrous metals, rare metals and nonmetals, and has been widely used in chemical industry, building materials, environmental protection, agriculture, medicine and other fields.
The Nile Machinery can provide a full set of process flow for flotation of non-metals and metals such as graphite, gold, silver, and copper.
Easy ways to get the answers you need. Service Online
What is froth flotation?
Flotation is a complex physical and chemical process completed in the three phase system of gas, liquid and solid. Its essence is that useful hydrophobic minerals adhere to the surface of the bubble and float, and hydrophilic gangue minerals remain in the pulp, so as to realize the separation of each other. The Nile Machinery can provide a full set of process flow for froth flotation of non-metals and metals such as graphite, gold, silver, and copper.
Flotation principle
Its main principle is to make one or a group of minerals in the ore selectively adhere to bubbles and float to the liquid surface by using the difference of physical and chemical properties of mineral surfaces, so as to separate useful minerals from gangue minerals. Because the separation process must be carried out in the pulp, it is called floating separation, which is called flotation for short.
It has the features of wide application range and strong adaptability. It can be used in various mineral departments such as nonferrous metals, rare metals and nonmetals, and has been widely used in chemical industry, building materials, environmental protection, agriculture, medicine and other fields.
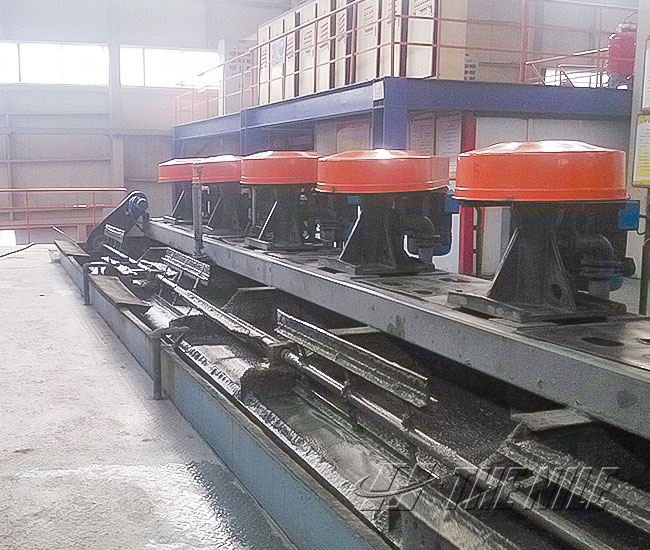


What is the purpose of flotation?
Enrich the target minerals in the raw ore, remove some harmful impurities, and reach the quality grade of the downstream users require .
 What kind of minerals are suitable for flotation?
What kind of minerals are suitable for flotation?
Flotation methods can be used for almost all ores. Most of the minerals that are difficult to recover or have low recovery rate by gravity separation and magnetic separation are recovered by flotation to recove the target minerals in the raw ore.
1. Precious metals such as the sulphide ore of gold and silver.
2. Sulphide ore such as galena, sphalerite, chalcopyrite, bornite, molybdenite, nickel sulfide and pyrite.
3. Non-ferrous metal oxides such as malachite, galena, hemimorphite, cassiterite, wolframite, ilmenite, beryl, spodumene and rare earth ore.
4. Elemental nonmetallic minerals such as graphite, sulfur and diamond.
5. Silicate minerals such as Shi Ying, mica, feldspar and other silicate minerals.
6. Non-metallic minerals such as fluorite, apatite and barite.
7. Iron oxide minerals, such as hematite, siderite and limonite.
8. Potassium salt, rock salt and other mineral salts.
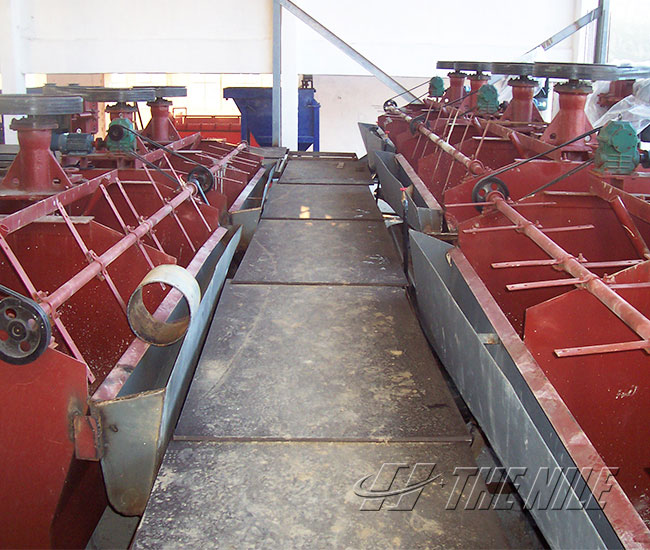


What are the main features of flotation?
1. It has the features of wide application range and strong adaptability.. It can be used in various mineral departments such as nonferrous metals, rare metals and nonmetals, and has been widely used in chemical industry, building materials, environmental protection, agriculture, medicine and other fields.
2. The separation efficiency is high, and it is suitable for treating minerals with low grade and fine embedment.
3. It is beneficial to the comprehensive recovery of mineral resources. The coarse concentrate, middling or tailings obtained by other mineral processing methods can be further treated to improve the concentrate grade, recovery rate and comprehensive recovery of useful components.
4. the shortcomings of flotation method, To be used various reagents, easy to cause environmental pollution; Need finer grinding particle size; High cost, many influencing factors and high technological requirements.
Positive flotation: In the process of flotation, useful minerals (target minerals) are floated into the foam products, while gangue minerals (waste rocks and impurities) are left in the pulp. This method is called positive flotation.
Reverse flotation: in the process of flotation, gangue minerals are floated into foam products, and useful minerals are left in pulp. This method is called reverse flotation.
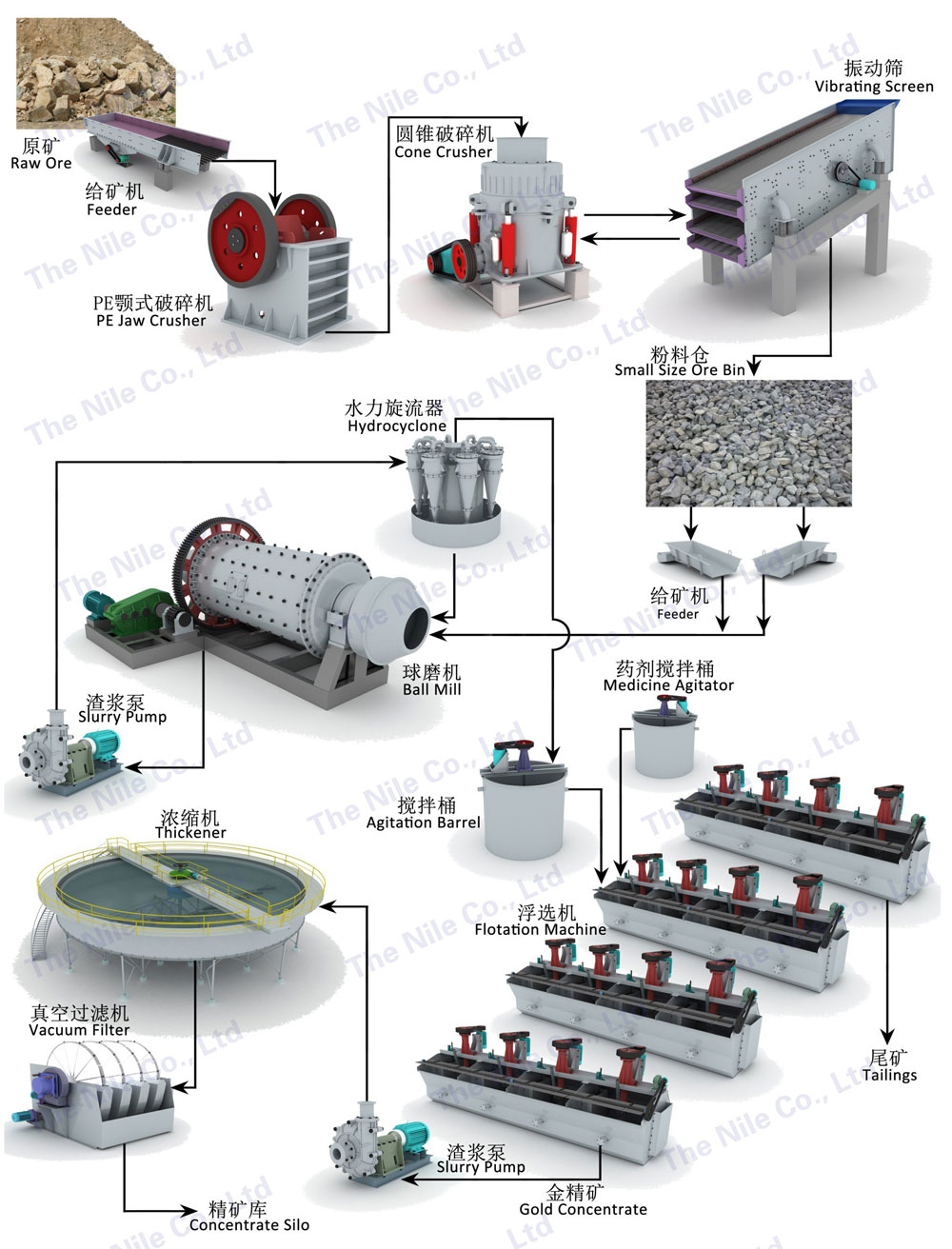
Flotation is a complex physical and chemical process completed in the three phase system of gas, liquid and solid. Its essence is that useful hydrophobic minerals adhere to the surface of the bubble and float, and hydrophilic gangue minerals remain in the pulp, so as to realize the separation of each other. The Nile Machinery can provide a full set of process flow for froth flotation of non-metals and metals such as graphite, gold, silver, and copper.
Its main principle is to make one or a group of minerals in the ore selectively adhere to bubbles and float to the liquid surface by using the difference of physical and chemical properties of mineral surfaces, so as to separate useful minerals from gangue minerals. Because the separation process must be carried out in the pulp, it is called floating separation, which is called flotation for short.
It has the features of wide application range and strong adaptability. It can be used in various mineral departments such as nonferrous metals, rare metals and nonmetals, and has been widely used in chemical industry, building materials, environmental protection, agriculture, medicine and other fields.


What is the purpose of flotation?
Enrich the target minerals in the raw ore, remove some harmful impurities, and reach the quality grade of the downstream users require .

Flotation methods can be used for almost all ores. Most of the minerals that are difficult to recover or have low recovery rate by gravity separation and magnetic separation are recovered by flotation to recove the target minerals in the raw ore.
1. Precious metals such as the sulphide ore of gold and silver.
2. Sulphide ore such as galena, sphalerite, chalcopyrite, bornite, molybdenite, nickel sulfide and pyrite.
3. Non-ferrous metal oxides such as malachite, galena, hemimorphite, cassiterite, wolframite, ilmenite, beryl, spodumene and rare earth ore.
4. Elemental nonmetallic minerals such as graphite, sulfur and diamond.
5. Silicate minerals such as Shi Ying, mica, feldspar and other silicate minerals.
6. Non-metallic minerals such as fluorite, apatite and barite.
7. Iron oxide minerals, such as hematite, siderite and limonite.
8. Potassium salt, rock salt and other mineral salts.


What are the main features of flotation?
1. It has the features of wide application range and strong adaptability.. It can be used in various mineral departments such as nonferrous metals, rare metals and nonmetals, and has been widely used in chemical industry, building materials, environmental protection, agriculture, medicine and other fields.
2. The separation efficiency is high, and it is suitable for treating minerals with low grade and fine embedment.
3. It is beneficial to the comprehensive recovery of mineral resources. The coarse concentrate, middling or tailings obtained by other mineral processing methods can be further treated to improve the concentrate grade, recovery rate and comprehensive recovery of useful components.
4. the shortcomings of flotation method, To be used various reagents, easy to cause environmental pollution; Need finer grinding particle size; High cost, many influencing factors and high technological requirements.
Positive flotation: In the process of flotation, useful minerals (target minerals) are floated into the foam products, while gangue minerals (waste rocks and impurities) are left in the pulp. This method is called positive flotation.
Reverse flotation: in the process of flotation, gangue minerals are floated into foam products, and useful minerals are left in pulp. This method is called reverse flotation.

Request for Quotation
You can get the price list and a NILE representative will contact you within one business day.






 WhatsApp
WhatsApp E-mail
E-mail Chat Now
Chat Now