What Are the Common Processes for Graphite Beneficiation?
One. Graphite Raw Ore Types
Industrially, natural graphite is classified into three categories according to different crystalline forms: dense crystalline graphite, flake graphite and cryptocrystalline graphite. Graphite ore can be further divided into crystalline graphite, flake graphite and graphite ore accompanied by a variety of gangues.
1、Dense crystalline graphite
Dense crystalline graphite, also called massive graphite, is mainly composed of dense crystalline graphite and plagioclase, quartz, as well as tremolite and chlorite. This kind of graphite crystallisation is obvious, the crystals can be seen by naked eyes, the particles are larger than 0.1mm, the arrangement of crystals is disordered, presenting dense crystalline structure. This kind of graphite is characterised by high grade, generally with carbon content of 60-65%, sometimes up to 80-98%, but its plasticity and slipperiness are not as good as that of flake graphite.
Massive graphite is the rarest and most valuable graphite ore, found mainly in Sri Lanka.
In some areas of China, we develop crystalline graphite, like Inner Mongolia, Heilongjiang, Shandong, Hebei, Henan, Hubei, Sichuan and other 16 provinces (autonomous regions). The important original places are Jixi and Laobei in Heilongjiang, Pingdu and Laixi in Shandong, Xinghe in Inner Mongolia, Chicheng in Hebei, Neixiang in Henan, Yichang in Hubei and Nanjiang in Sichuan.
2、Flake graphite
Flake graphite refers to natural crystalline graphite, which is shaped like fish scales, and is obtained from crystalline (scalar) graphite ores through processing, beneficiation, and some purified products. Flake graphite ores are mainly composed of minerals such as flake graphite, feldspar, quartz, diopside, tremolite, mica, etc. The graphite is in the form of scales or blades, and there is also a distinction between large scales and small scales. Flake graphite is formed by combining many single layers of graphite, and exists as individual flakes in metamorphic rocks, with small reserves and high value, and the crystals are in the form of scales, which are metamorphosed under high-intensity pressure.
The feature of this graphite ore is low grade, generally ranging from 2 to 3%, or 10 to 25%. It is one of the ores with the best floatability in nature, and high grade graphite concentrate can be obtained after multiple grinding and selection.
This type of graphite is superior to other types of graphite in terms of floatability, lubricity, and plasticity, so it has the greatest industrial value.
Flake graphite is mainly distributed in Australia, Brazil, Canada, China, Germany and Madagascar. In recent years, a large amount of flake graphite resources have also been found in Tanzania and Mozambique in Africa. Some scholars have studied the flake graphite ores in Ancuaba of Mozambique and Chilalo of Tanzania, and the results show that the mineral composition of graphite ores in Ancuaba and Chilalo are similar, and all of them are high-quality large flake graphite resources.
3、Cryptocrystalline graphite
Cryptocrystalline graphite is also called earthy graphite, its graphite crystals are small, generally less than 1μm, is a collection of microcrystals, must be visible under the microscope crystal shape.
Cryptocrystalline graphite ores are mainly composed of cryptocrystalline graphite, sericite, quartz, pyrite, calcite, limonite, clay and other minerals. This type of ore is characterized by an earthy surface, lack of luster and poor lubricity, but the ore grade is high. The general 60-85%, a few up to 90% or more. Generally it used in the foundry industry. With the improvement of graphite purification, earthy graphite is more and more widely used.
Earthy graphite have largest reserves, making up a large proportion of graphite deposits, with more than half of the world's total graphite production. With small scales and low crystalline, earthy graphite is used to produce low value products, making it the least expensive of the 3 types of graphite.
Earthy graphite is mainly found in Turkey, China, Europe, Mexico and the United States.
Two. Distribution and use of graphite by type
1. Graphite distribution by type
According to statistics results in 2015, global graphite reserves in total of 23,000,000,000 tons, of which Turkey's reserves are 90,000,000,000 tons, accounting for 39.13% of the global reserves, Brazil 72,000,000,000 tons for 31.30% of the global reserves, and China 55,000,000,000 tons, for 23.91% of the global reserves.
Typology Dense crystalline graphite (Massive graphite) Flake graphite Earthy graphite (Cryptocrystalline graphite)
Crystalline state (physics) Excellent Prefer Bad
Crystalline size >0.1 mm 0.05 to 1.5 mm (>1.0 μm) 0.01 to 0.1μm
Grade 60% to 65%, up to 80% to 98%. 2 to 5%, or between 10 and 25% 60 to 80%, a few up to 90 per cent or more
Floatability Good Good Bad
the source (of a product) (formerly) Ceylon Australia, Brazil, Canada, China, Germany and Madagascar Turkey, Europe, China, Mexico and the United States
2. Main uses of graphite
Graphite can be used to produce refractory materials, conductive materials, wear-resistant materials, lubricants, high-temperature-resistant sealing materials, corrosion-resistant materials, heat-insulating materials, adsorbent materials, friction materials, and radiation-resistant materials, etc., which are widely used in metallurgy, petrochemistry, the machinery industry, the electronics industry, the nuclear industry and national defence.
In recent years, due to the rapid development and promotion of new energy vehicles, the power battery industry has been developing rapidly, and the demand for graphite as a battery anode material has increased dramatically, especially the commercial value of large flake graphite.
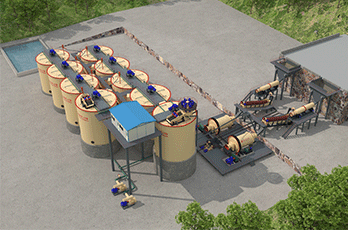
Three. Graphite beneficiation process
Graphite ore is metamorphosed by high pressure, generally greenish grey, yellowish brown or greyish white after weathering, its symbiotic minerals are more complex, mainly accompanied by feldspar, quartz, black mica, pyrite, magnetopyrite, rutile and other impurity minerals. According to the characteristics of flake graphite ore deposits and the different nature of the ore, its purification method is different, its purification methods are flotation purification, alkaline acid purification, hydrofluoric acid purification, chlorination roasting purification and high temperature.
Graphite contains impurities, mainly potassium, sodium, magnesium, calcium, aluminium and other silicate minerals, graphite purification process is to take effective means to remove this part of the impurities. At present, the main methods of graphite purification are flotation, alkaline acid method, hydrofluoric acid method, chlorination roasting method, high temperature method, etc..
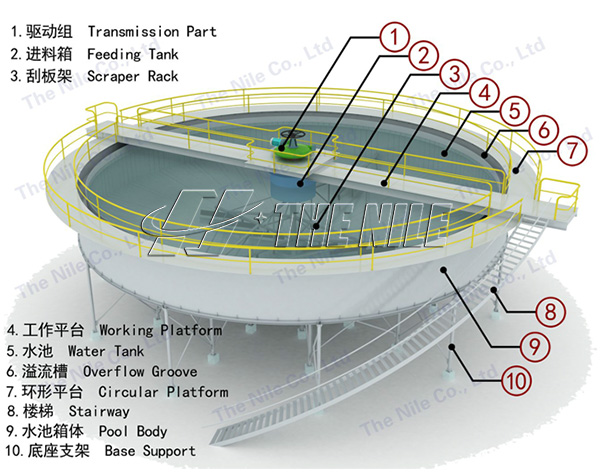
(i) Flotation
Flotation is a commonly used and important mineral processing method, graphite has good natural floatability, basically all graphite can be purified by flotation, in order to protect the graphite scales, graphite flotation mostly adopts multi-stage process. Flotation capture agent is generally used paraffin, the dosage is 100-200g/t, and the foaming agent is generally used turpentine oil or butyl ether oil, the dosage is 50-250g/t.
Because of the good natural floatability of graphite, the method can increase the grade of graphite to 80 to 90 per cent and even up to about 95 per cent. The greatest advantage of this method is that it has the lowest energy and reagent consumption and the lowest cost of all purification methods.
Inclusion in the graphite scale in a very fine state of silicate minerals and potassium, calcium, sodium, magnesium, aluminium and other elements of the compound, with the grinding method can not be dissociated from its monomer, and is not conducive to the protection of graphite large scale. Therefore, flotation method is only the primary means of graphite purification, if you want to obtain high carbon graphite with carbon content of 99% or more, you must use other methods of purification.
(ii) Alkaline-acid method
The alkaline-acid method consists of two reaction processes: the alkali fusion process and the acid leaching process.
1、alkali fusion process
Under high temperature conditions, molten state of alkali and graphite in the acidic impurities in the chemical reaction, especially silicon-containing impurities (such as silicate, silica-aluminate, quartz, etc.), to generate soluble salts, and then wash to remove impurities, so that graphite purity can be improved.
The process of alkali melting is to mix a certain amount of graphite, sodium hydroxide and water, put them into the reactor and heat them to melt. After a period of reaction, it is cooled to below 100°C and filtered until the pH of the aqueous solution is 7-8.
2、Acid leaching process
The basic principle of the acid leaching process is to use acid to react with metal oxide impurities, which do not react with alkali during the alkaline fusion process. The metal oxides are converted into soluble salts, which are then washed to separate them from the graphite.
Acid digestion process is the graphite after alkali dissolved (melting) and a certain concentration of hydrochloric acid solution mixed with hot dip filtration, after a period of time at a certain temperature reaction, filtration and water washing to neutral, drying, purification, through the acid digestion that is obtained after high purity graphite.
After the combination of alkali fusion and acid leaching has a better effect on graphite purification.
The alkaline-acid method mostly uses NaOH, which has a low melting point and is highly alkaline.The acid used in the acid leaching process can be HCl, H2SO4, HNO3 or their mixtures, of which HCl is used more often.
3、Integrated recovery of silicon
Alkali fusion purification of graphite, for some graphite with high silicon content, alkali fusion purification of graphite can also achieve the comprehensive recycling of silicon.
4、Advantages and disadvantages
Alkaline-acid is the most widely used method in the industrial production of graphite purification in our country, which has the characteristics of less one-time investment, higher product grade and strong adaptability, as well as the advantages of simple equipment and strong versatility.
The disadvantages are the need for high-temperature calcination, high energy consumption, long process flow, serious corrosion of equipment, graphite loss and serious pollution of wastewater.
(iii) Hydrofluoric acid method
Hydrofluoric acid is a strong acid that can react with almost any impurities in graphite, and graphite has good acid resistance, especially to hydrofluoric acid, which determines that graphite can be purified with hydrofluoric acid.
1、workflows
The main process of hydrofluoric acid method is that graphite and hydrofluoric acid are mixed, hydrofluoric acid and impurities react for a period of time to produce soluble substances or volatiles, the impurities are removed by washing, and the purified graphite is obtained after dehydration and drying.
2、Insufficient advantages of hydrofluoric acid
Insufficient advantages of hydrofluoric acid: Hydrofluoric acid reacts with Ca, Mg, Fe and other metal oxides to produce a precipitate, resulting in H2SiF6 dissolved in the solution, and can remove Ca, Mg, Fe and other impurities. Hydrofluoric acid is highly toxic, serious pollution of the environment, with other acids for graphite purification, can effectively reduce the amount of hydrofluoric acid.
Advantages: Hydrofluoric acid method of graphite purification has the advantages of simple process, high product grade, relatively low cost, and small impact on the performance of graphite products.
However, hydrofluoric acid is highly toxic and must have safety protection measures in the process of use, and the waste water produced must be treated before it is discharged to the outside, otherwise it will cause serious pollution to the environment.
(iv) Chlorination roasting
1、Principle of Chlorination Roasting
Chlorination roasting method refers to the graphite in high temperature and specific atmosphere roasting, and through the chlorine gas, so that the graphite impurities in the chlorination reaction, the generation of gas phase or condensate chlorination and complexes (lower melting and boiling point) to escape, so as to achieve purification.
Chlorination roasting is used to purify graphite by using the feature that the melting and boiling points of the impurity oxides are higher than those of the impurity chlorides.
2、Advantages and disadvantages of chlorination roasting
Advantages of the chlorination roasting method: in terms of energy saving, high purification efficiency (>98 per cent) and high recovery rate, but there are also problems such as toxic chlorine gas, serious corrosiveness and serious pollution of the environment.
Shortcomings: limited purity of graphite produced in the process, poor process stability, affecting the application of its method in actual production, and further improvements and enhancements are needed.
(v) High-temperature purification
The melting point of graphite is 3850℃±50℃, which is one of the substances with the highest melting and boiling point in nature, much higher than the boiling point of impurity silicate. Using the difference of their melting and boiling points, graphite is placed in a graphitised crucible and heated up to 2700°C under a certain atmosphere using specific instrumentation, which enables the impurities to gasify and escape from the graphite, achieving the effect of purification. This technology can purify graphite to more than 99.99%. Only graphite used in national defence, aerospace, nuclear industry and other high-tech fields are purified by this method.
1, Influence factors of graphite purification using high temperature method :
(1) Impurity content among graphite raw materials has the greatest impact on the effect of high-temperature purification method. Its different impurity content of raw materials, the finished ash content is different, and the graphite with a high content of carbon purification effect is better, high-temperature method is often used in the flotation method or alkaline-acid method of graphite purification after the carbon content reaches 99% and above as raw materials;
(2) The carbon content of graphite crucible is also an important factor affecting the purification effect, and the ash content of crucible is lower than that of graphite, which helps the ash in graphite to escape;
(3) The use of high current, graphite heating fast, conducive to the purification of graphite, it is best to use high-power electrode raw materials, and by 2800 ℃ high temperature treatment;
(3) Graphite particle size also has an effect on the purification effect.
2、Melting and boiling points of major oxide impurities in graphite
Graphite is a substance with high melting point and high boiling point, its melting and boiling point is much higher than the silicate minerals, the boiling point of silicate is 2750 ℃, graphite boiling point of 4500 ℃, melting point of 3850 ± 50 ℃.
(vi) Cryptocrystalline graphite processing
Cryptocrystalline graphite ore is high grade, but difficult to sort, many graphite mines will extract the ore directly for crushing and processing, selling graphite powder products.
Cryptocrystalline graphite crystals are extremely small, so it is also called microcrystalline graphite, graphite particles are often embedded in the clay, separation is very difficult. Due to the high grade of the original ore (generally containing 60% to 80% carbon), so many graphite mines will be extracted from the ore directly crushed and processed to sell graphite powder products. Hunan Lutang graphite mine was established in the 1950s flotation plant flotation microcrystalline graphite, but because the cost is too high and discontinued. At present, some units are still in the microcrystalline graphite flotation of new processes (such as oil agglomeration flotation, etc.) research.
Cryptocrystalline Graphite Ore Beneficiation Process: although cryptocrystalline graphite ore has high grade, it is difficult to be sorted. In China, it is usually mined graphite ore after simple selection artificial, directly crushed into products for sale. The general process is: raw ore → coarse crushing → medium crushing → drying → grinding → classification → packaging.
Industrially, natural graphite is classified into three categories according to different crystalline forms: dense crystalline graphite, flake graphite and cryptocrystalline graphite. Graphite ore can be further divided into crystalline graphite, flake graphite and graphite ore accompanied by a variety of gangues.
1、Dense crystalline graphite
Dense crystalline graphite, also called massive graphite, is mainly composed of dense crystalline graphite and plagioclase, quartz, as well as tremolite and chlorite. This kind of graphite crystallisation is obvious, the crystals can be seen by naked eyes, the particles are larger than 0.1mm, the arrangement of crystals is disordered, presenting dense crystalline structure. This kind of graphite is characterised by high grade, generally with carbon content of 60-65%, sometimes up to 80-98%, but its plasticity and slipperiness are not as good as that of flake graphite.
Massive graphite is the rarest and most valuable graphite ore, found mainly in Sri Lanka.
In some areas of China, we develop crystalline graphite, like Inner Mongolia, Heilongjiang, Shandong, Hebei, Henan, Hubei, Sichuan and other 16 provinces (autonomous regions). The important original places are Jixi and Laobei in Heilongjiang, Pingdu and Laixi in Shandong, Xinghe in Inner Mongolia, Chicheng in Hebei, Neixiang in Henan, Yichang in Hubei and Nanjiang in Sichuan.
2、Flake graphite
Flake graphite refers to natural crystalline graphite, which is shaped like fish scales, and is obtained from crystalline (scalar) graphite ores through processing, beneficiation, and some purified products. Flake graphite ores are mainly composed of minerals such as flake graphite, feldspar, quartz, diopside, tremolite, mica, etc. The graphite is in the form of scales or blades, and there is also a distinction between large scales and small scales. Flake graphite is formed by combining many single layers of graphite, and exists as individual flakes in metamorphic rocks, with small reserves and high value, and the crystals are in the form of scales, which are metamorphosed under high-intensity pressure.
The feature of this graphite ore is low grade, generally ranging from 2 to 3%, or 10 to 25%. It is one of the ores with the best floatability in nature, and high grade graphite concentrate can be obtained after multiple grinding and selection.
This type of graphite is superior to other types of graphite in terms of floatability, lubricity, and plasticity, so it has the greatest industrial value.
Flake graphite is mainly distributed in Australia, Brazil, Canada, China, Germany and Madagascar. In recent years, a large amount of flake graphite resources have also been found in Tanzania and Mozambique in Africa. Some scholars have studied the flake graphite ores in Ancuaba of Mozambique and Chilalo of Tanzania, and the results show that the mineral composition of graphite ores in Ancuaba and Chilalo are similar, and all of them are high-quality large flake graphite resources.
Cryptocrystalline graphite is also called earthy graphite, its graphite crystals are small, generally less than 1μm, is a collection of microcrystals, must be visible under the microscope crystal shape.
Cryptocrystalline graphite ores are mainly composed of cryptocrystalline graphite, sericite, quartz, pyrite, calcite, limonite, clay and other minerals. This type of ore is characterized by an earthy surface, lack of luster and poor lubricity, but the ore grade is high. The general 60-85%, a few up to 90% or more. Generally it used in the foundry industry. With the improvement of graphite purification, earthy graphite is more and more widely used.
Earthy graphite have largest reserves, making up a large proportion of graphite deposits, with more than half of the world's total graphite production. With small scales and low crystalline, earthy graphite is used to produce low value products, making it the least expensive of the 3 types of graphite.
Earthy graphite is mainly found in Turkey, China, Europe, Mexico and the United States.
1. Graphite distribution by type
According to statistics results in 2015, global graphite reserves in total of 23,000,000,000 tons, of which Turkey's reserves are 90,000,000,000 tons, accounting for 39.13% of the global reserves, Brazil 72,000,000,000 tons for 31.30% of the global reserves, and China 55,000,000,000 tons, for 23.91% of the global reserves.
Typology Dense crystalline graphite (Massive graphite) Flake graphite Earthy graphite (Cryptocrystalline graphite)
Crystalline state (physics) Excellent Prefer Bad
Crystalline size >0.1 mm 0.05 to 1.5 mm (>1.0 μm) 0.01 to 0.1μm
Grade 60% to 65%, up to 80% to 98%. 2 to 5%, or between 10 and 25% 60 to 80%, a few up to 90 per cent or more
Floatability Good Good Bad
the source (of a product) (formerly) Ceylon Australia, Brazil, Canada, China, Germany and Madagascar Turkey, Europe, China, Mexico and the United States
2. Main uses of graphite
Graphite can be used to produce refractory materials, conductive materials, wear-resistant materials, lubricants, high-temperature-resistant sealing materials, corrosion-resistant materials, heat-insulating materials, adsorbent materials, friction materials, and radiation-resistant materials, etc., which are widely used in metallurgy, petrochemistry, the machinery industry, the electronics industry, the nuclear industry and national defence.
In recent years, due to the rapid development and promotion of new energy vehicles, the power battery industry has been developing rapidly, and the demand for graphite as a battery anode material has increased dramatically, especially the commercial value of large flake graphite.
Three. Graphite beneficiation process
Graphite ore is metamorphosed by high pressure, generally greenish grey, yellowish brown or greyish white after weathering, its symbiotic minerals are more complex, mainly accompanied by feldspar, quartz, black mica, pyrite, magnetopyrite, rutile and other impurity minerals. According to the characteristics of flake graphite ore deposits and the different nature of the ore, its purification method is different, its purification methods are flotation purification, alkaline acid purification, hydrofluoric acid purification, chlorination roasting purification and high temperature.
Graphite contains impurities, mainly potassium, sodium, magnesium, calcium, aluminium and other silicate minerals, graphite purification process is to take effective means to remove this part of the impurities. At present, the main methods of graphite purification are flotation, alkaline acid method, hydrofluoric acid method, chlorination roasting method, high temperature method, etc..
(i) Flotation
Flotation is a commonly used and important mineral processing method, graphite has good natural floatability, basically all graphite can be purified by flotation, in order to protect the graphite scales, graphite flotation mostly adopts multi-stage process. Flotation capture agent is generally used paraffin, the dosage is 100-200g/t, and the foaming agent is generally used turpentine oil or butyl ether oil, the dosage is 50-250g/t.
Because of the good natural floatability of graphite, the method can increase the grade of graphite to 80 to 90 per cent and even up to about 95 per cent. The greatest advantage of this method is that it has the lowest energy and reagent consumption and the lowest cost of all purification methods.
Inclusion in the graphite scale in a very fine state of silicate minerals and potassium, calcium, sodium, magnesium, aluminium and other elements of the compound, with the grinding method can not be dissociated from its monomer, and is not conducive to the protection of graphite large scale. Therefore, flotation method is only the primary means of graphite purification, if you want to obtain high carbon graphite with carbon content of 99% or more, you must use other methods of purification.
| Typology | Dense crystalline graphite (Massive graphite) | Flake graphite | Earthy graphite (Cryptocrystalline graphite) |
| Crystalline state (physics) | Excellent | Prefer | Bad |
| Crystalline size | >0.1 mm | 0.05 to 1.5 mm (>1.0 μm) | 0.01 to 0.1μm |
| Grade | 60% to 65%, up to 80% to 98%. | 2 to 5%, or between 10 and 25% | 60 to 80%, a few up to 90 per cent or more |
| Floatability | Good | Good | Bad |
| the source (of a product) | (formerly) Ceylon | Australia, Brazil, Canada, China, Germany and Madagascar | Turkey, Europe, China, Mexico and the United States |
(ii) Alkaline-acid method
The alkaline-acid method consists of two reaction processes: the alkali fusion process and the acid leaching process.
1、alkali fusion process
Under high temperature conditions, molten state of alkali and graphite in the acidic impurities in the chemical reaction, especially silicon-containing impurities (such as silicate, silica-aluminate, quartz, etc.), to generate soluble salts, and then wash to remove impurities, so that graphite purity can be improved.
The process of alkali melting is to mix a certain amount of graphite, sodium hydroxide and water, put them into the reactor and heat them to melt. After a period of reaction, it is cooled to below 100°C and filtered until the pH of the aqueous solution is 7-8.
2、Acid leaching process
The basic principle of the acid leaching process is to use acid to react with metal oxide impurities, which do not react with alkali during the alkaline fusion process. The metal oxides are converted into soluble salts, which are then washed to separate them from the graphite.
Acid digestion process is the graphite after alkali dissolved (melting) and a certain concentration of hydrochloric acid solution mixed with hot dip filtration, after a period of time at a certain temperature reaction, filtration and water washing to neutral, drying, purification, through the acid digestion that is obtained after high purity graphite.
After the combination of alkali fusion and acid leaching has a better effect on graphite purification.
The alkaline-acid method mostly uses NaOH, which has a low melting point and is highly alkaline.The acid used in the acid leaching process can be HCl, H2SO4, HNO3 or their mixtures, of which HCl is used more often.
3、Integrated recovery of silicon
Alkali fusion purification of graphite, for some graphite with high silicon content, alkali fusion purification of graphite can also achieve the comprehensive recycling of silicon.
4、Advantages and disadvantages
Alkaline-acid is the most widely used method in the industrial production of graphite purification in our country, which has the characteristics of less one-time investment, higher product grade and strong adaptability, as well as the advantages of simple equipment and strong versatility.
The disadvantages are the need for high-temperature calcination, high energy consumption, long process flow, serious corrosion of equipment, graphite loss and serious pollution of wastewater.
(iii) Hydrofluoric acid method
Hydrofluoric acid is a strong acid that can react with almost any impurities in graphite, and graphite has good acid resistance, especially to hydrofluoric acid, which determines that graphite can be purified with hydrofluoric acid.
1、workflows
The main process of hydrofluoric acid method is that graphite and hydrofluoric acid are mixed, hydrofluoric acid and impurities react for a period of time to produce soluble substances or volatiles, the impurities are removed by washing, and the purified graphite is obtained after dehydration and drying.
2、Insufficient advantages of hydrofluoric acid
Insufficient advantages of hydrofluoric acid: Hydrofluoric acid reacts with Ca, Mg, Fe and other metal oxides to produce a precipitate, resulting in H2SiF6 dissolved in the solution, and can remove Ca, Mg, Fe and other impurities. Hydrofluoric acid is highly toxic, serious pollution of the environment, with other acids for graphite purification, can effectively reduce the amount of hydrofluoric acid.
Advantages: Hydrofluoric acid method of graphite purification has the advantages of simple process, high product grade, relatively low cost, and small impact on the performance of graphite products.
However, hydrofluoric acid is highly toxic and must have safety protection measures in the process of use, and the waste water produced must be treated before it is discharged to the outside, otherwise it will cause serious pollution to the environment.
(iv) Chlorination roasting
1、Principle of Chlorination Roasting
Chlorination roasting method refers to the graphite in high temperature and specific atmosphere roasting, and through the chlorine gas, so that the graphite impurities in the chlorination reaction, the generation of gas phase or condensate chlorination and complexes (lower melting and boiling point) to escape, so as to achieve purification.
Chlorination roasting is used to purify graphite by using the feature that the melting and boiling points of the impurity oxides are higher than those of the impurity chlorides.
2、Advantages and disadvantages of chlorination roasting
Advantages of the chlorination roasting method: in terms of energy saving, high purification efficiency (>98 per cent) and high recovery rate, but there are also problems such as toxic chlorine gas, serious corrosiveness and serious pollution of the environment.
Shortcomings: limited purity of graphite produced in the process, poor process stability, affecting the application of its method in actual production, and further improvements and enhancements are needed.
(v) High-temperature purification
The melting point of graphite is 3850℃±50℃, which is one of the substances with the highest melting and boiling point in nature, much higher than the boiling point of impurity silicate. Using the difference of their melting and boiling points, graphite is placed in a graphitised crucible and heated up to 2700°C under a certain atmosphere using specific instrumentation, which enables the impurities to gasify and escape from the graphite, achieving the effect of purification. This technology can purify graphite to more than 99.99%. Only graphite used in national defence, aerospace, nuclear industry and other high-tech fields are purified by this method.
1, Influence factors of graphite purification using high temperature method :
(1) Impurity content among graphite raw materials has the greatest impact on the effect of high-temperature purification method. Its different impurity content of raw materials, the finished ash content is different, and the graphite with a high content of carbon purification effect is better, high-temperature method is often used in the flotation method or alkaline-acid method of graphite purification after the carbon content reaches 99% and above as raw materials;
(2) The carbon content of graphite crucible is also an important factor affecting the purification effect, and the ash content of crucible is lower than that of graphite, which helps the ash in graphite to escape;
(3) The use of high current, graphite heating fast, conducive to the purification of graphite, it is best to use high-power electrode raw materials, and by 2800 ℃ high temperature treatment;
(3) Graphite particle size also has an effect on the purification effect.
2、Melting and boiling points of major oxide impurities in graphite
Graphite is a substance with high melting point and high boiling point, its melting and boiling point is much higher than the silicate minerals, the boiling point of silicate is 2750 ℃, graphite boiling point of 4500 ℃, melting point of 3850 ± 50 ℃.
Cryptocrystalline graphite ore is high grade, but difficult to sort, many graphite mines will extract the ore directly for crushing and processing, selling graphite powder products.
Cryptocrystalline graphite crystals are extremely small, so it is also called microcrystalline graphite, graphite particles are often embedded in the clay, separation is very difficult. Due to the high grade of the original ore (generally containing 60% to 80% carbon), so many graphite mines will be extracted from the ore directly crushed and processed to sell graphite powder products. Hunan Lutang graphite mine was established in the 1950s flotation plant flotation microcrystalline graphite, but because the cost is too high and discontinued. At present, some units are still in the microcrystalline graphite flotation of new processes (such as oil agglomeration flotation, etc.) research.
Cryptocrystalline Graphite Ore Beneficiation Process: although cryptocrystalline graphite ore has high grade, it is difficult to be sorted. In China, it is usually mined graphite ore after simple selection artificial, directly crushed into products for sale. The general process is: raw ore → coarse crushing → medium crushing → drying → grinding → classification → packaging.
Request for Quotation
You can get the price list and a NILE representative will contact you within one business day.







 WhatsApp
WhatsApp E-mail
E-mail Chat Now
Chat Now